National Health Information Exchange
Shareable Health Records (SHR) System Bangladesh
The Shareable Health Record (SHR) system is a Centralized Digital system of the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare that identifies each citizen with Basic info and demography, can fetch their Visits & service records from different points of Care, Generate Personal Health Profile and share medical records on demand with consent.
Unique Health ID (HID) Registrations by Platform
Health ID Registered
Regs. via OpenMRS+
Regs. via OpenSRP
Regs. via Aalo Clinic
Regs. via eMIS
Clinical Records by Platform
Total Clinical Records
Records via OpenMRS+
Records via OpenSRP
Records via Aalo Clinic
Records via eMIS
Core Components
- Hospital Management System
- Health ID
- Health Information Exchange
- Personal Health Profile
- Data Security and Privacy
Hospital Automation Systems is one of the major components of the Shareable Health Record System implemented by the Management Information System (MIS) under the HIS and e-Health Operational Plan of the Directorate of Health, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. The hospital automation system is the use of information technology or digital systems in all hospital operations and coordination between them to ensure proper quality service at a low cost and at the appropriate time.
For Public hospitals, Bangladesh uses open source Open MRS with few customizations and calls it Open MRS+.
For the private sector, they can use their solution. If any Private Hospital wants to use our package they can use it.
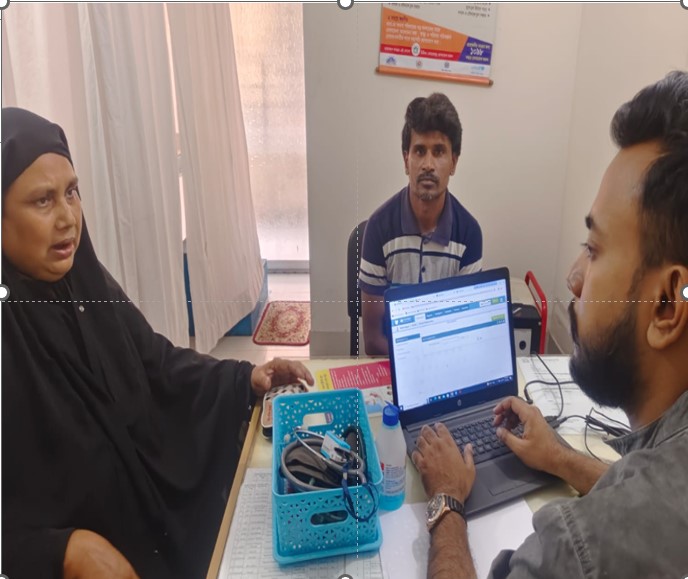
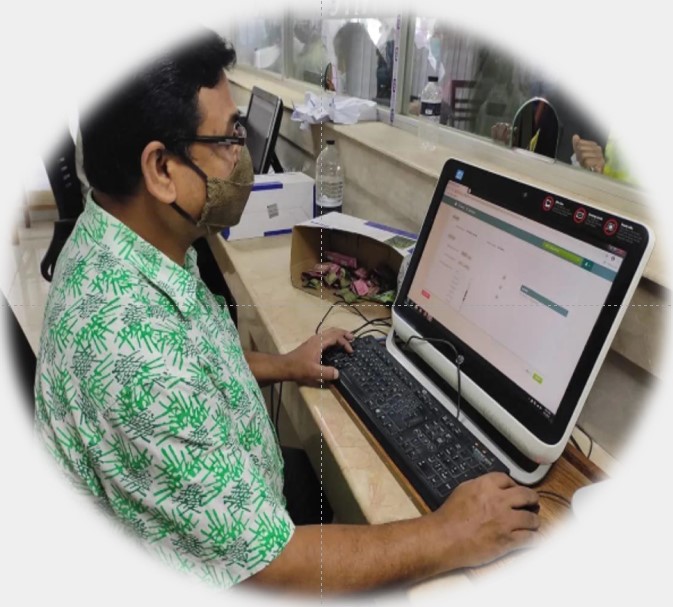
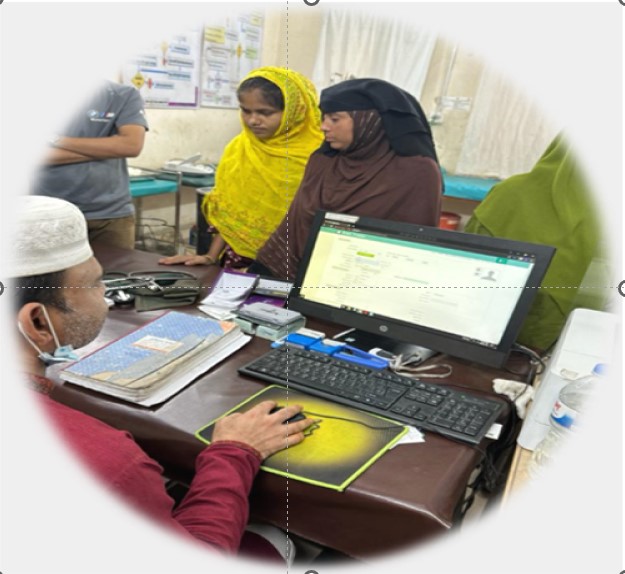
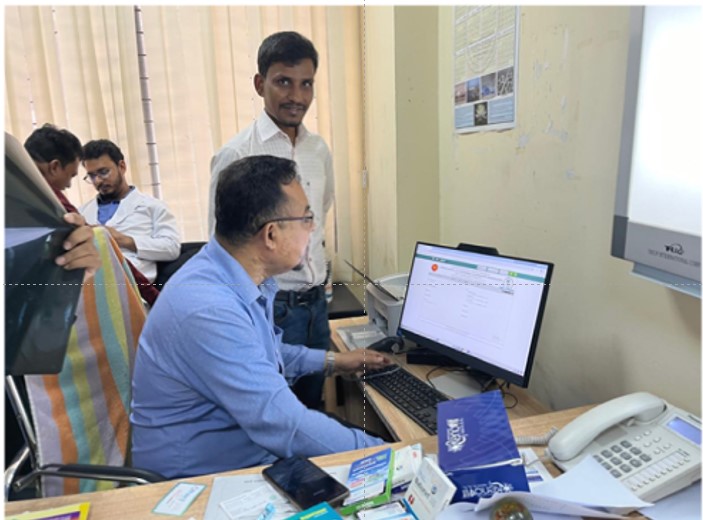




Unique Health ID is a process of digitally identifying every citizen of all age groups, which will help all healthcare providers and institutions identify the same person and provide services. A health card containing this ID number will be issued to the citizen.

Health Information Exchange (HIE) is the process of electronically moving health-related information among organizations. The goal is to facilitate access to and retrieval of clinical data to provide better patient care, improve public health, and reduce administrative overhead.
All health care institutions including public and private hospitals/clinics, diagnostic centers, private chambers, pharmacies, telemedicine centers will use their respective electronic medical records and hospital automation systems.
Data from these systems will be linked to a central health profile by assigning a single unique identifier- the Health ID. as well as using the Standards and registries.
Persona Health Profile
This central Personal health profile will include all the health services a citizen receives and all the healthcare providers or institutions (Government/non-government / NGO Facilities and Private chambers) they visit throughout their lifetime (from birth to death). A citizen’s Electronic Health Record (EHR) is called Personal Health Profile, where all encounters will be available. Citizens will have access to this profile. The owner of this information is the citizen. He/She can share their Health data with his Health Care provider electronically at present within the country
Since all their medical history, medical records, and investigation reports are stored electronically, the citizen and their healthcare providers can repeatedly access them, significantly reducing hassle, time, and cost. There will be no need to maintain and carry paper files for medical history, records, and investigation reports. Ensuring the availability and transparency of all information will improve the relationship between the patient and the doctor, increasing trust in the healthcare system. Both the patient and the doctor will be safer in medicolegal matters.
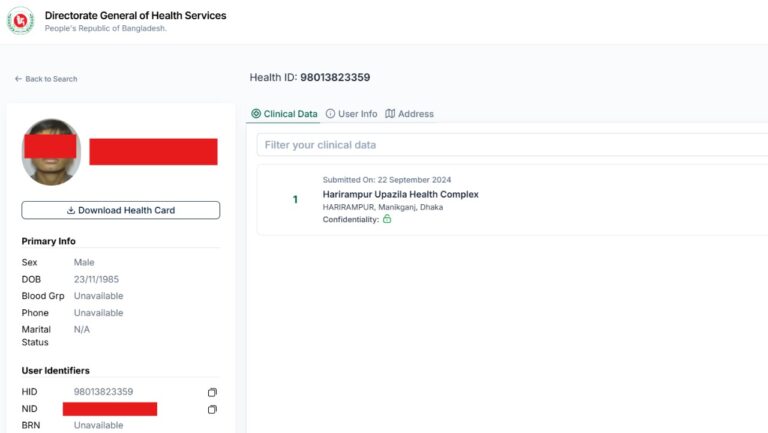
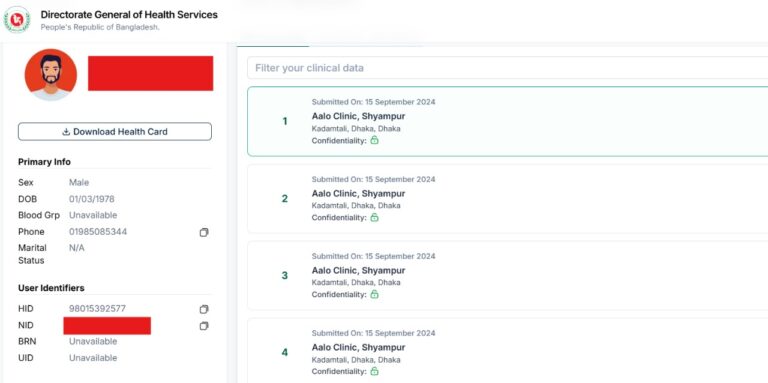
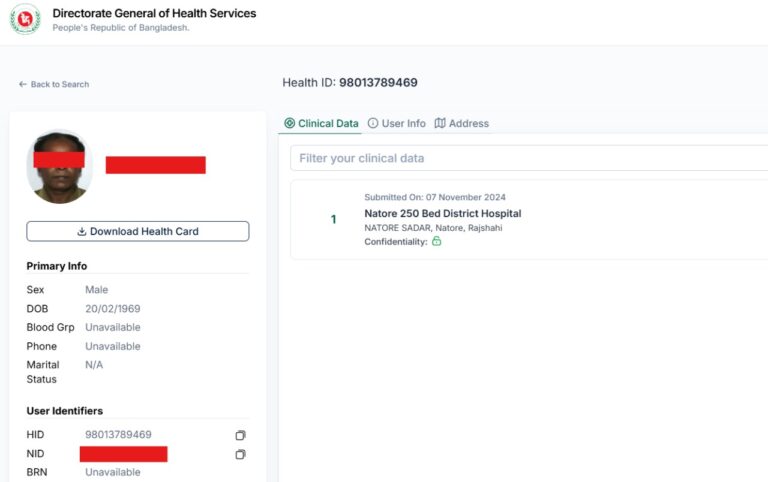
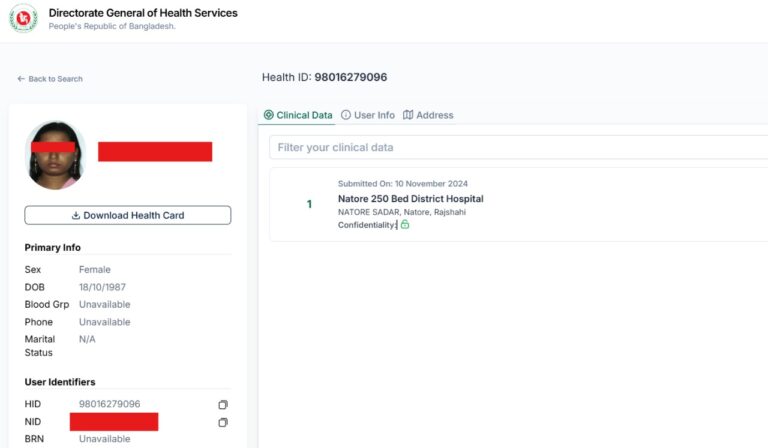
Data security is crucial in the context of interoperability and health information exchange (HIE). Achieving effective interoperability and health information exchange, ensuring that patient data is protected, trust is maintained, and regulatory requirements are met. We are addressing the following issues:
Protecting Patient Privacy and Consent Management: Ensuring that patient information is kept confidential is paramount. Robust security measures, such as encryption, authentication, and access controls, are essential to safeguard patient data. Data sharing would not happen without patients’ consent.
Maintaining Trust: Patients and healthcare providers need to trust that their data is secure. This trust is vital for the successful adoption and use of HIE systems.
Compliance with Regulations: Adhering to privacy regulations, such as HIPAA in the United States, is mandatory. These regulations require stringent data security measures to protect patient information.
Preventing Data Breaches: Data breaches can have severe consequences, including financial loss, legal repercussions, and damage to reputation. Effective data security measures help prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
Facilitating Seamless Data Exchange: Secure data exchange is essential for interoperability. It ensures that data can be shared across different healthcare systems without compromising security.
Supporting Informed Decision-Making: Secure access to comprehensive patient data enables healthcare providers to make informed decisions, leading to better patient outcomes.




